We have talked about almost 36 of Google’s proven and speculated factors that contribute towards a website’s SERP.
Last few weeks we have talked about,
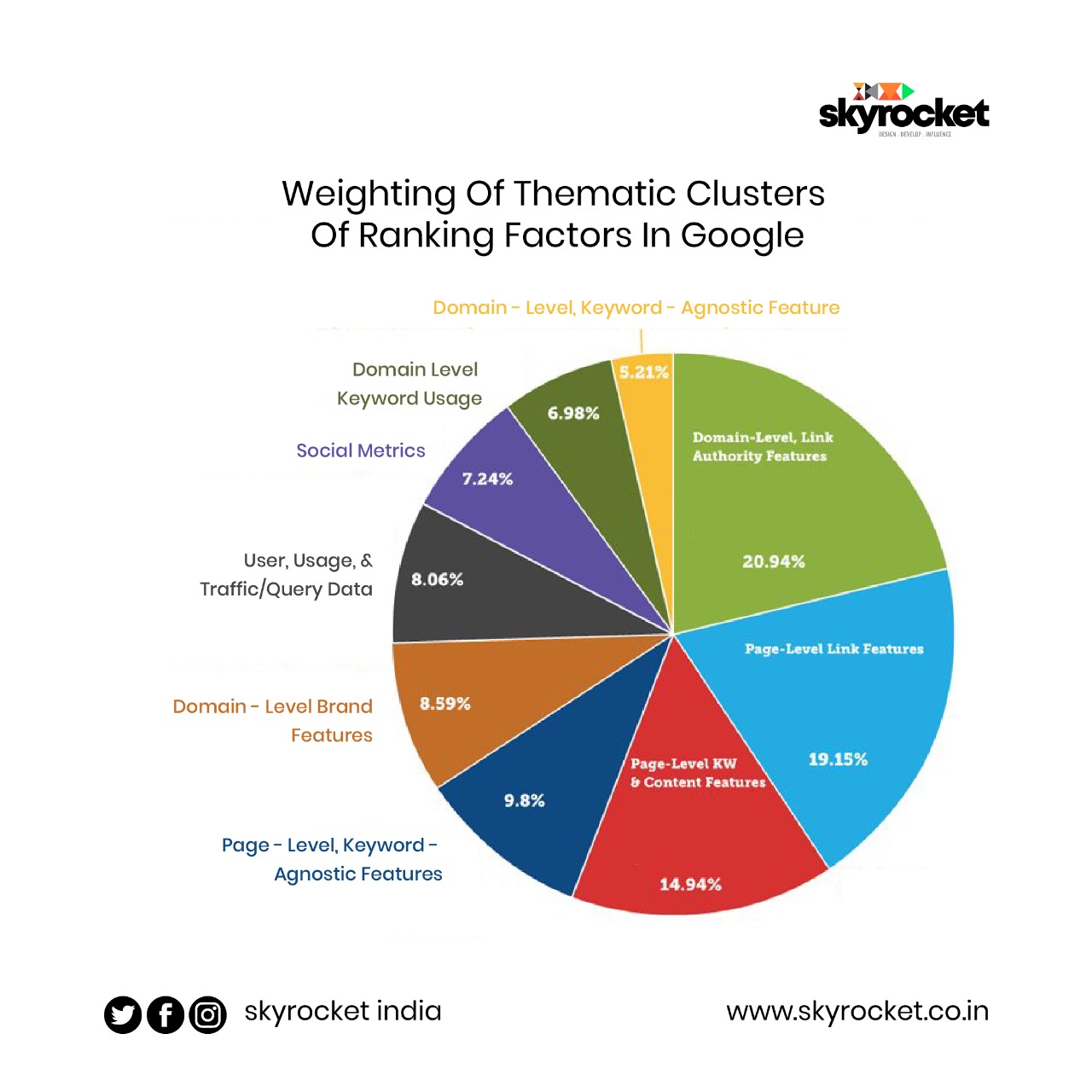
- The amount of weightage given by google for various page-ranking factors.
Followed by the,
2. Domain Level factors that influence your SERP rank.
and…
3. Page-level factors that influence your SERP.
Today we are going to talk about the remaining…
Page-level factors that influence your SERP followed by the Site level factors.
- Number of Internal Links Pointing to Page (more internal links=more important): Internal links from authoritative pages on domain have a stronger effect than pages with no or low PageRank.
- Broken Links: This may be a sign of a neglected or abandoned site. The Google Rater Guidelines Document uses broken links as one way to assess a homepage’s quality.
- Reading Level: Although not clear if and how this affects the algorithm. This is definitely something google can measure about your page.
- Affiliate Links: Affiliate links won’t hurt your rankings. But like everything else this too can backfire on your SERP when used too much.
- HTML errors/W3C validation: A lot of coding errors could be considered the sign of a bad website.
- Domain Authority: All things being equal, a page on an authoritative domain will rank higher than a page on a domain with less authority.
- URL Length: Several industry studies have found that short URLs tend to perform better than long URLs.
- URL Path: The deeper the path of your page the harder it is for it to get indexed by search engines.
- Human Editors: Although it does not directly contribute to SERP. Google does use Human Editors to evaluate the top ranking pages and verify that whatever results Google’s algorithm ranked is accurate and relevant to the search term.
- WordPress Tags: Tags are WordPress-specific relevancy signal.
- Keyword in URL: Can be considered a minor relevancy signal.
- References and Sources: Citing references and sources, like research papers do, may be a sign of quality.
- Bullets and Numbered Lists: Bullets and numbered lists help break up your content for readers, making them more user friendly.
- Priority of Page in Sitemap: The priority a page is given via the sitemap.xml file may influence ranking.
- UX Signals From Other Keywords Page Ranks For: If the page ranks for several other keywords, it may give Google an internal sign of quality. In fact, Google’s “How Search Works” report states: “We look for sites that many users seem to value for similar queries.”
- Page Age: Fresh content is given priority in google but however older pages which gets updated tend to perform better comparitively.
- User Friendly Layout: Citing Google Quality Guidelines Document: “The page layout on highest quality pages makes the Main Content immediately visible.”
- Parked Domains: A Google update decreased search visibility of parked domains.
- Useful Content: Google may distinguish between “quality” and “useful” content.
These are the page-level factors that influence your SERP. Now let’s look at the site level factors that influence your page-rank.
Site-Level Factors
- Contact Us Page: Make sure that your contact information matches your whois info.
- Domain Trust/TrustRank: Many SEOs believe that “TrustRank” is a massively important ranking factor. And a Google Patent titled “Search result ranking based on trust”, seems to back this up.
- Site Architecture: It helps Googlebot access and index all of your site’s pages.
- Site Updates: Website updates, especially when new content is added to the site — works a site-wide freshness factor. Although Google has recently denied that they use “publishing frequency” in their algorithm.
- Presence of Sitemap: A sitemap helps search engines index your pages easier and more thoroughly, improving visibility. However, Google recently stated that HTML sitemaps aren’t “useful” for SEO.
- Site Uptime: Lots of downtime from site maintenance or server issues may hurt your rankings (and can even result in deindexing if not corrected).
- Server Location: Server location influences where your site ranks in different geographical regions. Especially important for geo-specific searches.
- SSL Certificate: Google has confirmed that use HTTPS as a ranking signal.
- Terms of Service and Privacy Pages: They help improve your site’s E-A-T in Google.
- Duplicate Meta Information On-Site: Duplicate meta information across your site may bring down all of your page’s visibility.
- Breadcrumb Navigation: This is a style of user-friendly site-architecture that helps users (and search engines) know where they are on a site: “Google Search uses breadcrumb markup in the body of a web page to categorize the information from the page in search results.” – Google.
- Mobile Optimized: Google has recently started penalizing websites that aren’t mobile friendly
- YouTube: Google gives preference to YouTube videos in search, maybe because they own it. Especially after the Panda update.
These are the page level & site level factors which influence your SERP ranking. Come back again for more Site level factors that influence your SERP positions and more. Thanks for reading.
Source: Backlinko